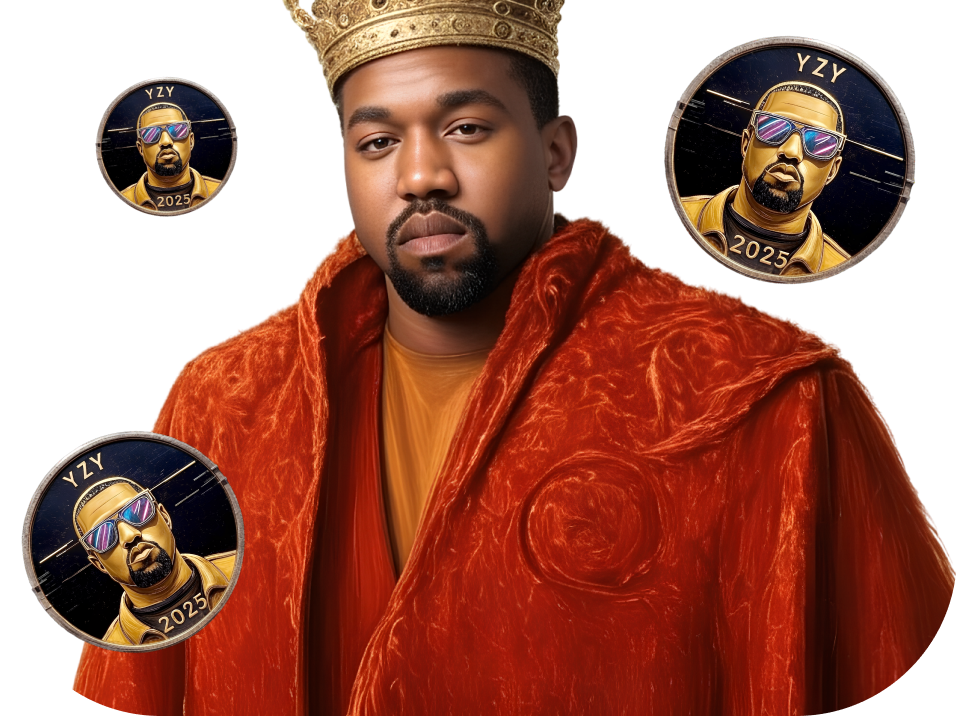
about airdrop
Official YZY
coin airdrop
The official Airdrop
from the YZY team

Available
For Everyone
each participant can
successfully claim a reward

23:59:45
$100.000

Q1 Airdrop
Users can claim
rewards along their
$100.000

Q2 Airdrop
Users will be able to get rewards
for their achievements later
$100.000

Q3 Airdrop
Users will be able to get rewards
for their achievements later

Participate now!
Don't miss your chance to get a YZY Coin
in the official airdrop from the YZY team
