Welcome to the intriguing world of lie detector tests. For years, these tests have captivated our imagination, offering a glimpse into the mysterious realm of human deception. At the core of every polygraph examination lies the fundamental question: Can we truly uncover the truth buried within the intricate web of human lies and deceit? The enigmatic nature of lie detectors leads us on a quest to unravel the complexities that define their essence and efficacy. Join us on a journey as we uncover the hidden truths behind this fascinating realm of deception detection.
History of Lie Detector Tests
Lie detector tests have a long and intriguing history that dates back to the early 20th century. The concept of detecting deception by measuring physiological responses such as heart rate and blood pressure was first explored by psychologist William Moulton Marston.
In the 1920s, John Larson, a student of Marston, developed the first polygraph machine, which measured changes in blood pressure to determine if someone was lying. This invention paved the way for the modern lie detector tests used today in various fields, including law enforcement and security.
Over the years, lie detector tests have evolved to incorporate multiple physiological measurements, such as respiration and skin conductivity, to provide more accurate results. Despite ongoing debates about their reliability, these tests remain a widely used tool in uncovering the truth in various situations.
How Lie Detector Tests Work
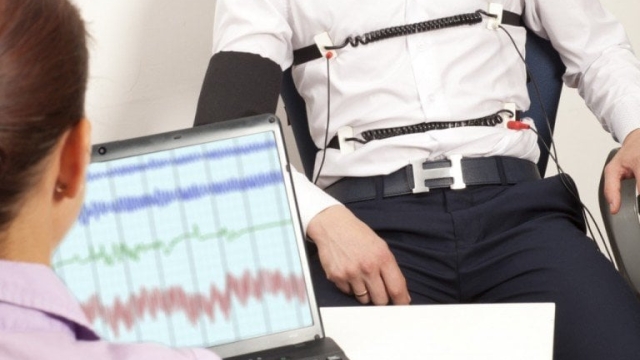
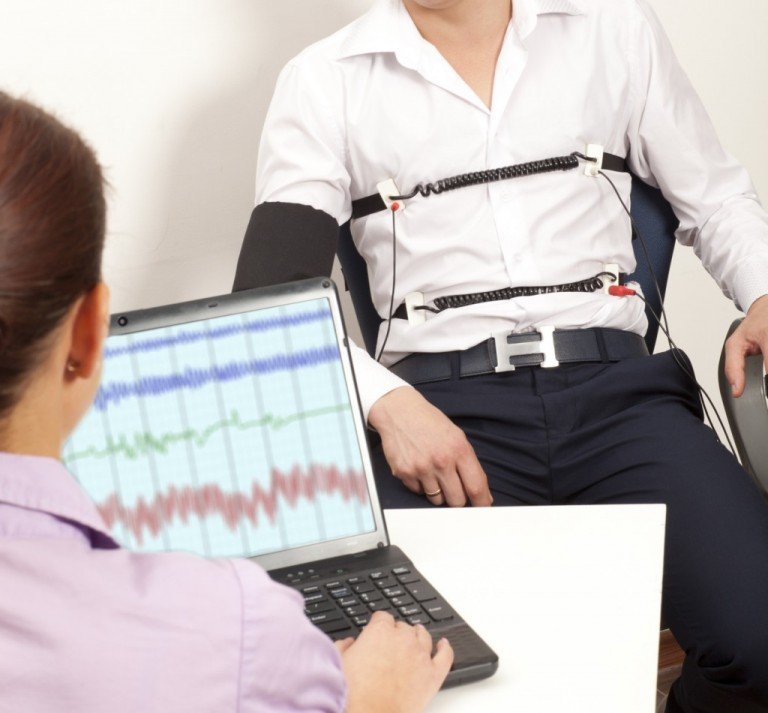
Lie detector tests, also known as polygraph examinations, are designed to detect physiological changes in a person when they are asked specific questions. These tests are based on the premise that when someone is being deceptive, their body will typically exhibit signs of stress or anxiety.
During a lie detector test, several sensors are attached to the person being examined to monitor their physiological responses. These sensors typically measure parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate, and skin conductivity.
Polygraph
As the individual answers a series of questions, the polygraph machine records the fluctuations in their physiological responses. These recordings are then analyzed by a trained examiner who interprets the data to determine the likelihood of deception.
Controversies Surrounding Lie Detector Tests
One controversy surrounding lie detector tests is their accuracy. Critics argue that the results can be influenced by various factors such as anxiety levels, personal beliefs, or the skill of the examiner.
Another point of contention is the legality of using lie detectors in certain situations. In many jurisdictions, lie detector results are not admissible as evidence in court due to concerns about reliability and potential for manipulation.
Furthermore, some ethical concerns have been raised regarding the use of lie detectors, particularly in employment settings. Critics argue that relying on these tests can lead to discrimination and violation of privacy rights.